News Center
0512-52836238
0512-52836128
0512-52358728
Sales Department Fax
0512-52836278
Sales Department Email
xu@worldbrom.com
Purchasing Department Tel/ Fax
0512-52836228
Headquarters Address US Office
, No. 18 Haitian Road, Advanced Material Industrial Park, Changshu City, Jiangsu
Tel
+1 832-857-1028
U.S. office mailbox
Lauren@worldbrom.com
shelia@worldbrom.com
U.S. office address
Creekside Park, The Woodlands, Texas 77375, USA
corporate website
www.worldbrom.com
Procurement Hotline
0512-52836128Sources:www.worldbrom.com | PublishDate:2025.10.15
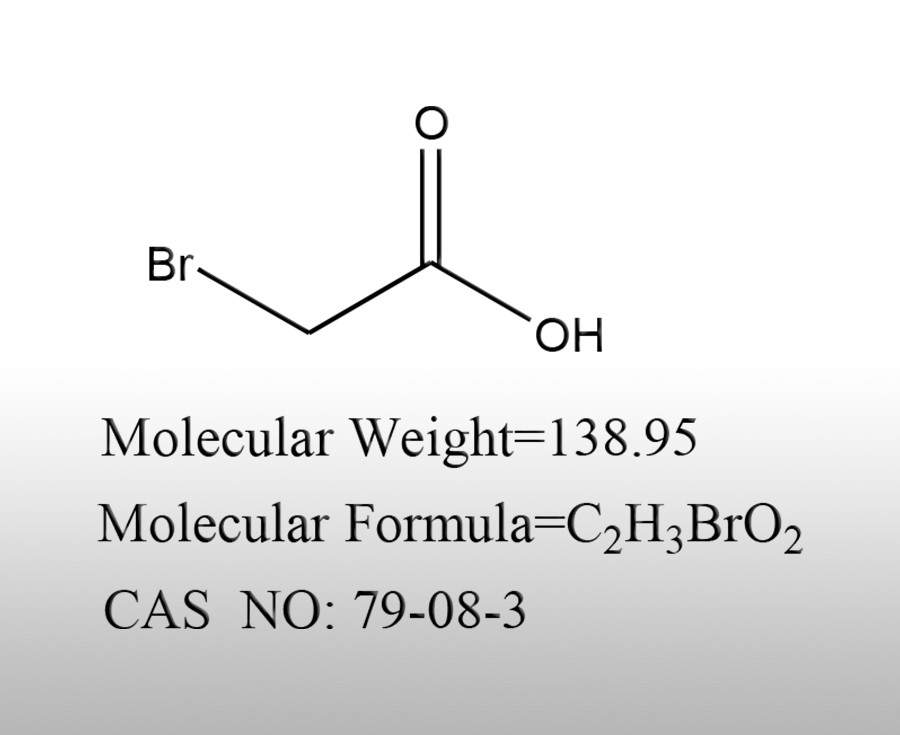
Bromoacetic acid, as a hazardous chemical with both corrosiveness and toxicity, must strictly comply with hazardous goods transportation regulations during transportation. The core is to prevent leakage, prevent contact, and control environmental risks. Specific precautions can be divided into five categories: transportation qualifications, packaging requirements, loading specifications, in-process control, and emergency response.
1. Transportation qualification: Must have legal and compliant transportation qualifications
The transportation unit needs to obtain a "Road Dangerous Goods Transport Permit", and the vehicle needs to hang a "Corrosive Goods" (the corrosive goods mark specified in GB 13690) and a "Dangerous Goods" dual warning sign. The body of the vehicle should be sprayed with the dangerous goods number (the United Nations number for bromoacetic acid is UN 1938).
Drivers and escorts need to undergo special training on dangerous goods transportation, obtain the "Qualification Certificate for Road Dangerous Goods Transport Practitioners", familiarize themselves with the hazardous characteristics and emergency response methods of bromoacetic acid, and strictly prohibit unlicensed transportation.
2. Packaging requirements: Ensure sealing without leakage, isolate external contact
Special packaging that meets relevant standards should be used, such as acid and alkali resistant polyethylene plastic drums (thickness not less than 5mm) or steel drums lined with anti-corrosion coatings. The drum mouth should be double sealed (threaded cover+sealing rubber ring) to prevent leakage caused by transportation bumps.
Clear hazardous material labels should be affixed outside the packaging, indicating the chemical name (bromoacetic acid), UN number, manufacturer, emergency contact information, and operation signs such as "Do not invert" and "Handle with care". The labels should be waterproof and wear-resistant to ensure clear and recognizable throughout transportation.
In case of little dose transportation (such as laboratory samples), buffer packaging (such as foam pads and shockproof cartons) shall be added outside the main packaging to avoid packaging damage caused by collision.
3. Loading specifications: Reasonably fix to avoid risks caused by mixed loading
Before loading, it is necessary to inspect the cargo compartment of the vehicle to ensure that there are no oil stains, water stains, or sharp debris. The bottom of the cargo compartment can be covered with acid and alkali resistant rubber pads or plastic film to prevent liquid from seeping into the compartment after packaging damage.
Bromoacetic acid needs to be loaded separately and is strictly prohibited from being mixed with strong bases (such as sodium hydroxide), strong oxidants (such as potassium permanganate), reducing agents (such as iron powder), as well as food, medicine, and daily necessities to avoid contact with different chemicals that may cause violent reactions (such as exothermic reactions, explosions) or contaminate other goods.
When loading, handle with care and do not throw or impact the packaging; The stacking height of the goods shall not exceed the height of the vehicle guardrail and shall be fixed with ropes or barriers to prevent the packaging from shifting or tipping due to bumps during transportation.
4. On the way control: Control the transportation environment and monitor the status in real time
Transportation routes need to be planned in advance, avoiding sensitive areas such as residential areas, schools, and water sources. It is strictly prohibited to stay in busy urban areas or highway service areas for a long time; The transportation time should avoid high temperature periods as much as possible (nighttime or early morning transportation is preferred in summer), to prevent high temperature from causing an increase in pressure inside the packaging and increasing the risk of leakage.
Vehicles need to be equipped with GPS positioning systems and real-time monitoring devices. Escorts need to regularly check the packaging status of goods (at least once every 2 hours), focusing on whether there are signs of leakage, bulging, or damage. If any abnormalities are found, immediately park in a safe area (away from fire sources, water sources, and crowds) and initiate emergency response.
Drivers are strictly prohibited from fatigue driving during transportation. They must rest in the dangerous goods parking area every 4 hours of driving. Tobacco and the use of open flames are prohibited in the vehicle. The vehicle must be equipped with fire extinguishing equipment (such as dry powder fire extinguishers) and anti-static grounding devices to prevent static electricity from causing danger.
5. Emergency response: Prepare contingency plans in advance and respond quickly to leaks
The vehicle must carry the MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet) for bromoacetic acid, emergency handling tools (such as absorbent cotton, sand, acid and alkali resistant gloves, goggles), and first aid drugs (such as weak alkaline neutralizers, burn ointment) with the vehicle. The escort must be proficient in the leakage handling process.
If there is a minor leak, immediately turn off the vehicle engine, wear protective equipment, and cover the leak area with absorbent cotton or dry sand. The adsorbed waste should be placed in a special sealed bag, labeled as "hazardous waste", and handed over to a qualified unit for disposal. It is strictly prohibited to discard or flow into the sewer or soil at will.
If a large amount of leakage or packaging damage occurs, immediately set up warning tapes around the leakage area, evacuate surrounding personnel, call the local emergency management department (such as 119, 122) and environmental protection department, and notify the transportation unit. Professional personnel should be present to handle the situation to avoid pollution expansion or causing poisoning or burns to personnel.