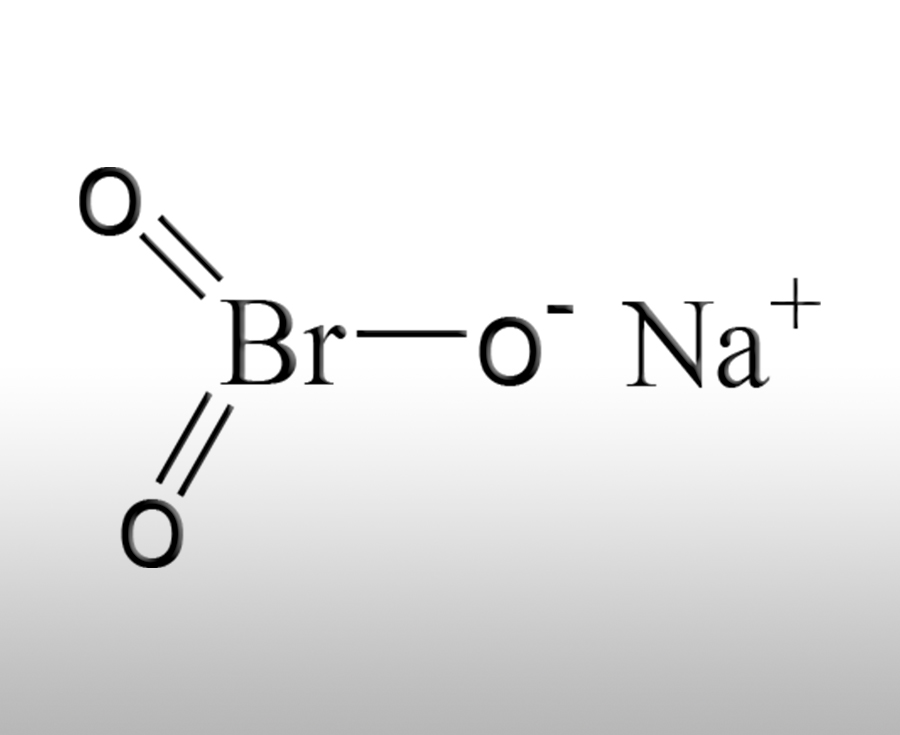News Center
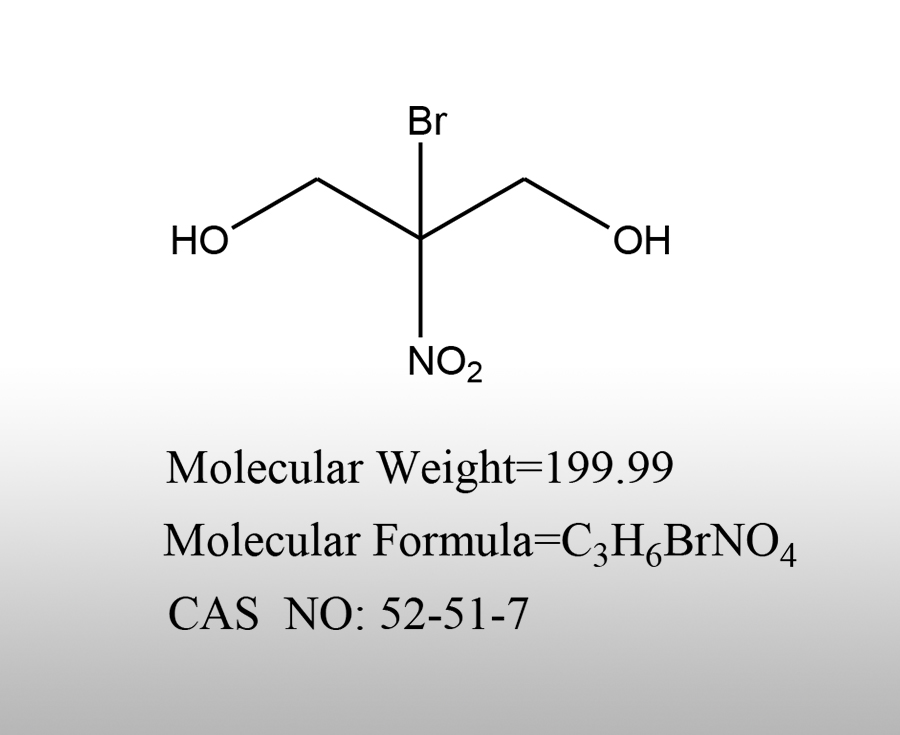
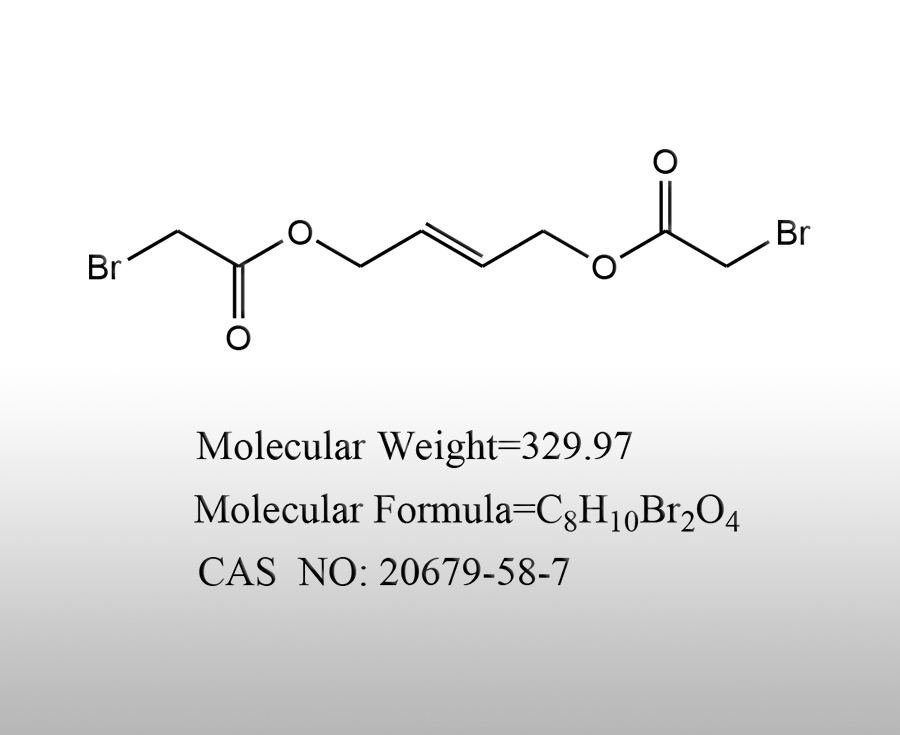
Popular products
Sales Department Tel:
0512-52836238
0512-52836128
0512-52358728
Sales Department Fax
0512-52836278
Sales Department Email
xu@worldbrom.com
Purchasing Department Tel/ Fax
0512-52836228
Headquarters Address US Office
, No. 18 Haitian Road, Advanced Material Industrial Park, Changshu City, Jiangsu
Tel
+1 832-857-1028
U.S. office mailbox
Lauren@worldbrom.com
shelia@worldbrom.com
U.S. office address
Creekside Park, The Woodlands, Texas 77375, USA
corporate website
www.worldbrom.com
0512-52836238
0512-52836128
0512-52358728
Sales Department Fax
0512-52836278
Sales Department Email
xu@worldbrom.com
Purchasing Department Tel/ Fax
0512-52836228
Headquarters Address US Office
, No. 18 Haitian Road, Advanced Material Industrial Park, Changshu City, Jiangsu
Tel
+1 832-857-1028
U.S. office mailbox
Lauren@worldbrom.com
shelia@worldbrom.com
U.S. office address
Creekside Park, The Woodlands, Texas 77375, USA
corporate website
www.worldbrom.com
Procurement Hotline
0512-52836128
What are the functions of sodium bromate in the chemical industry
Sodium bromate (NaBrO3) is an important chemical raw material with various functions in the chemical industry, mainly used in the following fields:Sources:www.worldbrom.com | PublishDate:2025.06.05
1、 Oxidizer
Sodium bromate has strong oxidizing properties and is commonly used in oxidation reactions in chemical synthesis. Specific applications include:
1. Organic synthesis
In the synthesis of intermediates in the fields of medicine, pesticides, dyes, etc., it participates in oxidation reactions as an oxidant. For example:
Oxidation of alcohol compounds to form aldehydes or ketones;
Preparation of quinone dye intermediates from oxidized aniline compounds;
Oxidation of sulfur-containing or nitrogen-containing compounds in pesticide synthesis to improve product purity.
Characteristics: Mild reaction conditions, controllable oxidation ability, suitable for selective oxidation reactions.
2. Polymer industry
In polymerization reactions such as acrylic ester and styrene, it is used as an initiator or oxidant to regulate the polymerization rate and product structure.
For example, in lotion polymerization, a redox initiator system is formed with a reducing agent (such as sulfite) to reduce the reaction temperature and improve the polymerization efficiency.
2、 Analytical chemical reagents
Sodium bromate is used as a standard reagent in laboratory analysis, mainly for:
1. Capacity analysis (titration method)
As a benchmark substance for calibrating the concentration of reducing agents (such as sodium thiosulfate and arsenite), quantitative analysis is carried out through the reduction reaction of bromate ions (such as BrO ∝⁻+6I ⁻+6H ⁺ → Br ⁻+3I ₂+3H ₂ O).
Widely used in environmental monitoring (such as determination of sulfides and nitrites in water) and purity testing of chemical products.
2. Sample pretreatment
In the digestion process of soil, ore and other samples, the oxidative decomposition of complex organic or reducing substances is utilized for subsequent elemental analysis (such as heavy metal detection).
3、 Water treatment and disinfection
Sodium bromate has specific applications in the field of water treatment, but attention should be paid to its toxicity and usage limitations:
1. Industrial wastewater treatment
Used for treating cyanide containing wastewater, phenolic wastewater, etc., and degrading toxic and harmful substances through oxidation reactions. For example:
Cyanide oxide (CN ⁻) generates non-toxic carbonate (CO ∝ ² ⁻) and nitrogen gas (N ₂), with the reaction equation:
2CN⁻ + 5BrO₃⁻ + 2H⁺ → 2CO₂↑ + N₂↑ + 5Br⁻ + H₂O
But the dosage needs to be strictly controlled to avoid secondary pollution caused by residual bromide ions (BrO ∝⁻) (bromate is a potential carcinogen with lower limits in drinking water standards).
2. Swimming pool disinfection (restricted use)
In the early days, it was used as a raw material for bromine containing disinfectants (reacting with sodium bromide to produce bromine), but due to the health risks of bromate, it has gradually been replaced by chlorine based disinfectants and is only used cautiously in specific industrial scenarios.
4、 Other applications
1. Ceramic and glass industry
In the preparation of ceramic glazes and glass colorants, as oxidants, the valence state of metal ions (such as iron and chromium) is adjusted, which affects the color and properties of the materials.
2. Pharmaceutical intermediates
In the synthesis route of certain drugs (such as antibiotics), as reagents in the oxidation step, they participate in the construction of key functional groups.