News Center
Popular products
Sales Department Tel:
0512-52836238
0512-52836128
0512-52358728
Sales Department Fax
0512-52836278
Sales Department Email
xu@worldbrom.com
Purchasing Department Tel/ Fax
0512-52836228
Headquarters Address US Office
, No. 18 Haitian Road, Advanced Material Industrial Park, Changshu City, Jiangsu
Tel
+1 832-857-1028
U.S. office mailbox
Lauren@worldbrom.com
shelia@worldbrom.com
U.S. office address
Creekside Park, The Woodlands, Texas 77375, USA
corporate website
www.worldbrom.com
0512-52836238
0512-52836128
0512-52358728
Sales Department Fax
0512-52836278
Sales Department Email
xu@worldbrom.com
Purchasing Department Tel/ Fax
0512-52836228
Headquarters Address US Office
, No. 18 Haitian Road, Advanced Material Industrial Park, Changshu City, Jiangsu
Tel
+1 832-857-1028
U.S. office mailbox
Lauren@worldbrom.com
shelia@worldbrom.com
U.S. office address
Creekside Park, The Woodlands, Texas 77375, USA
corporate website
www.worldbrom.com
Procurement Hotline
0512-52836128
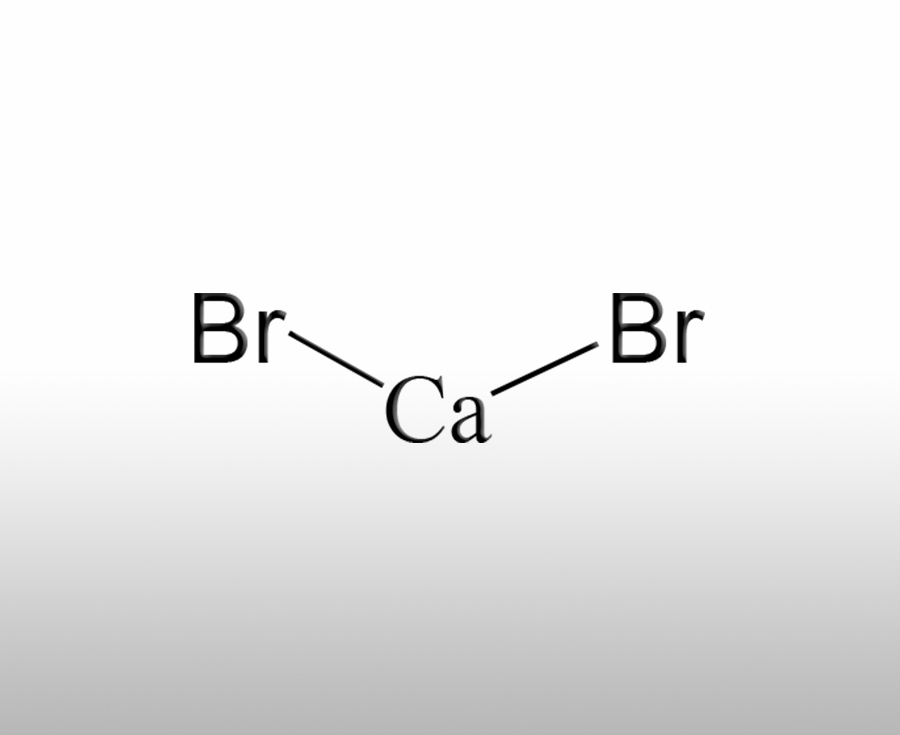
What are the characteristics of calcium bromide
Calcium bromide (CaBr ₂) is an important inorganic bromide with unique chemical properties and a wide range of application scenarios. Its main characteristics are as follows:Sources:www.worldbrom.com | PublishDate:2025.08.06
1. Stable chemical properties, easily soluble in water
Calcium bromide is an ionic compound composed of Ca ² ⁺ and Br ⁻. It is a white crystalline or granular solid at room temperature, odorless, and has a salty and slightly bitter taste.
It has extremely strong water solubility, and its solubility increases significantly with temperature (about 143g/100mL water at 20 ℃). Its aqueous solution is neutral or weakly alkaline.
Good stability, not easily decomposed in dry air, but deliquescent when in contact with water, so it needs to be sealed and stored; At high temperatures, it can decompose into hydrogen bromide and calcium oxide.
2. Has sedative and neuroprotective effects
Bromine ion (Br ⁻) is an inhibitor of the central nervous system. After entering the human body, calcium bromide can dissociate Br ⁻ and exert sedative, hypnotic, and anticonvulsant effects by reducing the excitability of nerve cells.
Medically, it has been used to treat neurasthenia, epilepsy, insomnia, etc., but due to side effects such as accumulation poisoning and affecting thyroid function, its clinical application has gradually decreased and is being replaced by safer drugs.
3. Wide range of industrial and oilfield applications
Oilfield drilling fluid additive: Calcium bromide solution has a high density (up to 1.8-2.3g/cm ³) and is the main component of high-density drilling fluid (completion fluid). It can balance formation pressure, prevent blowouts, and cause minimal damage to oil and gas reservoirs. It is suitable for deep and high-pressure oil and gas well operations.
Industrial flame retardants: When used in conjunction with other bromides, they can enhance the flame retardant properties of materials and are used for fire prevention treatment of plastics, textiles, and other materials.
Refrigerants and de icing agents: Their aqueous solutions have a low freezing point and can be used as auxiliary components of refrigerants; In road de icing, it can lower the melting point of ice and snow and improve de icing efficiency (but it is less commonly used due to its higher cost than calcium chloride).
4. Easy to react with other substances
Reacting with silver nitrate (AgNO3) produces a pale yellow precipitate of silver bromide (AgBr), which is the reaction for testing bromide ions:
CaBr₂ + 2AgNO₃ = 2AgBr↓ + Ca(NO₃)₂
When heated with concentrated sulfuric acid, an oxidation-reduction reaction occurs, producing bromine (Br ₂), calcium sulfate, and water, reflecting the reducibility of bromide ions.
5. Safety should be taken into consideration
Calcium bromide itself has low toxicity, but excessive intake can lead to bromine poisoning, symptoms such as headache, drowsiness, and mental confusion, and the dosage should be strictly controlled.
Its dust or solution is irritating to the eyes and skin, and should be rinsed with clean water in a timely manner after contact; When storing, it should be separated from strong acids and oxidants to avoid dangerous reactions.